In the course of 2022, our colleagues successfully completed an international scientific project System of more accurate prediction of convective precipitation over the regional territorial unit. It was a 3-year research project (2019 - 2022), sponsored by the Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic, led by the team of dr. David Šaur from Tomáš Baťa University in Zlín (Czech Republic).
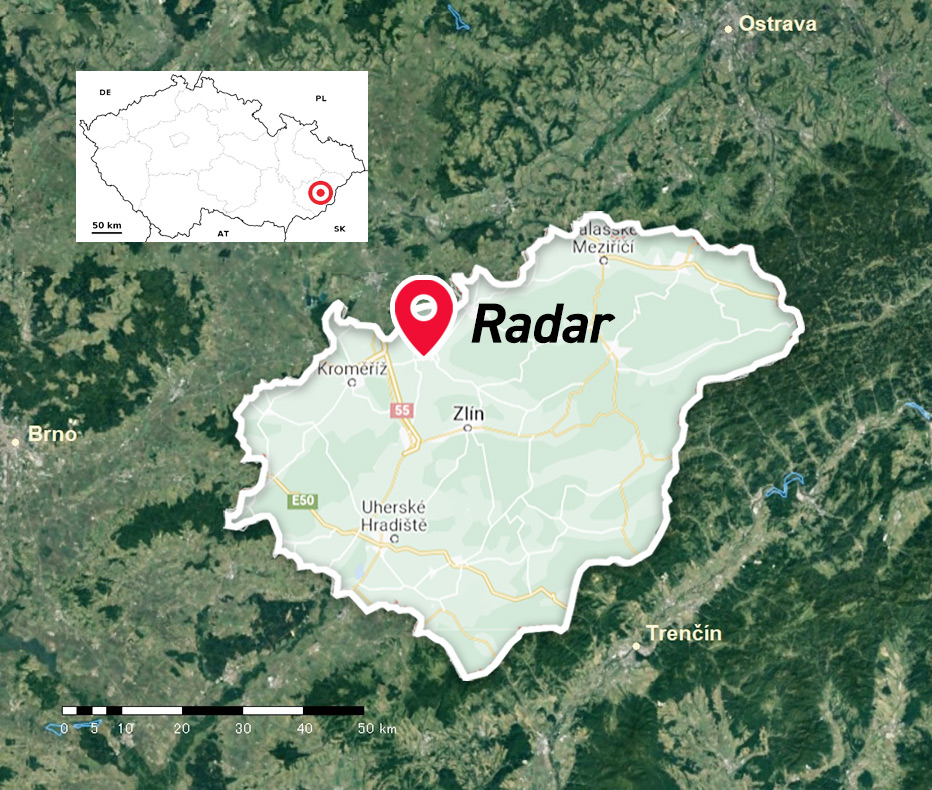
The goal of the project was to develop more accurate methods of predicting convective precipitation in the Czech Republic. The project consisted of two main parts. The first sub-part of the project (in the duty of the Czech colleagues) focused on the entire territory of the Czech Republic and developed methods for predicting the occurrence of convective precipitation up to 24 hours in advance based on statistical methods of multivariate analysis. The second sub-part of the project (assigned to the MicroStep-MIS team) was focused on a smaller territory (Zlín region, covering 13 municipalities with extended scope, MEP), shorter time horizons in the future (tens of minutes, up to 1 hour) and was aimed at providing nowcasts using the volume scans of the X-band radar located in the target region (Holešov, near the city of Zlín).
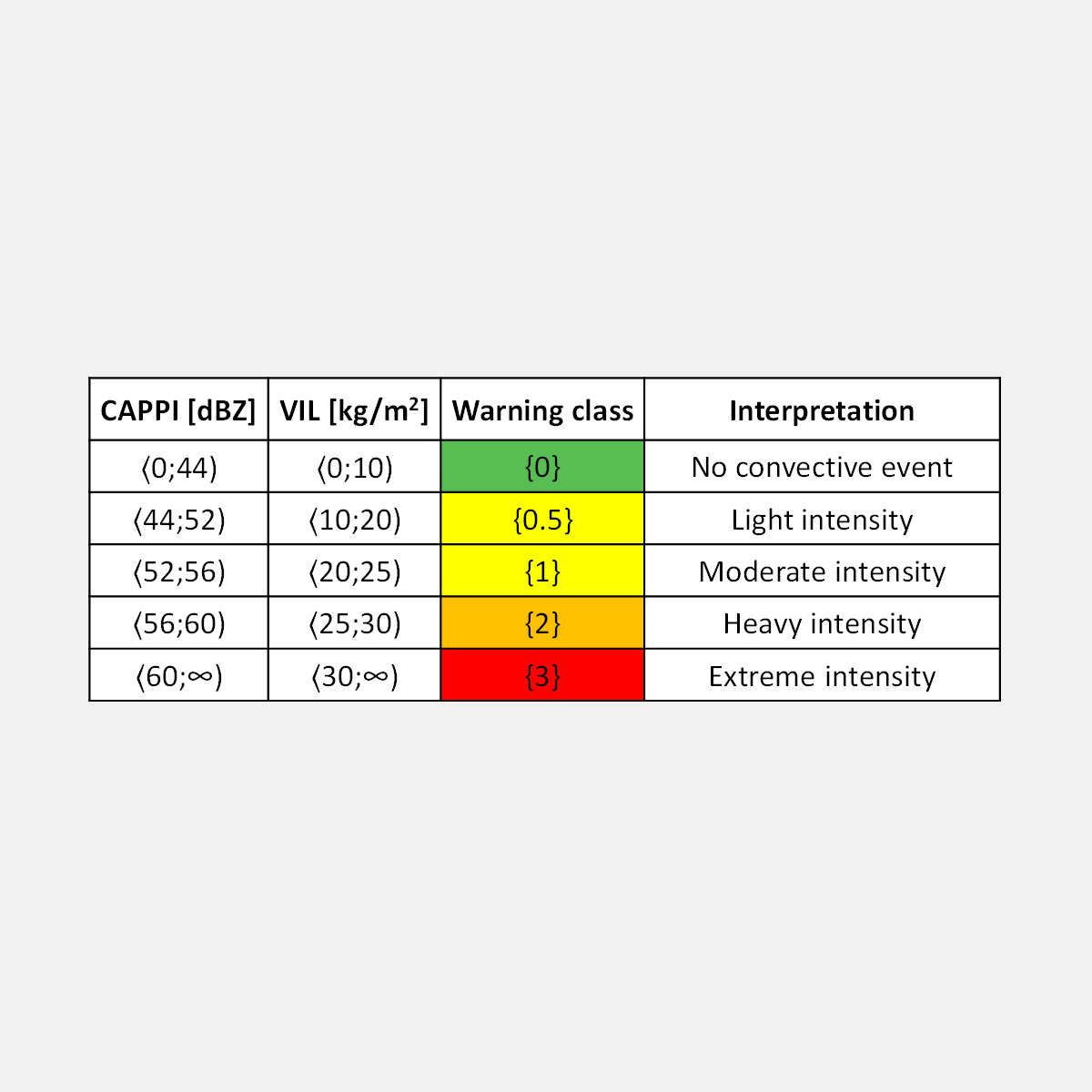
One of the specific features of the nowcasting was the fact that the forecasts were not expressed in terms of traditional radar reflectivity characteristics such as PCAPPI (Pseudo Constant Altitude Plain Position Indicator) and VIL (Vertically Integrated Liquid). Instead, they were converted into a 4-class system of qualitative classification, termed as warning classes, where ‘0’ indicated no convective event, ‘1’ was for light/moderate rainfall intensity, ‘2’ for rainfall of heavy intensity, and ‘3’ indicated extremely intense convective events. Moreover, instead of pixel-based nowcasts, a single value of warning class was derived for the individual MEPs in each time step of the prediction. Such a classification system is in line with the generally accepted approach of the units of crisis management as well as the Czech Hydrometeorological Institute where warnings on different meteorological, hydrological or other phenomena are expressed in terms of codes from 0 to 3, and are also visualized by green, yellow, orange, and red colors. The predicted warning classes are expected to indicate the required degree of preparedness of the staff of crisis management in the case of an upcoming convective rainfall event.
In the radar nowcasting, the performance of well-known methods of radar echo extrapolation (TITAN, COTREC) was examined, along with the baseline Persistence model, which simply assumes that the radar field does not change in the near future. In addition to this, various combinations of these approaches within the framework of machine learning were tested. The elaborated statistical evaluation of the constructed forecast models revealed that several of them showed more favorable performance than the TITAN model that is currently being used in an operational practice in the Zlín region. Finally, the combined model of the COTREC and Persistence methods was selected as the overall best one. The analysis further confirmed that the upper limit of the nowcast models is about 30 - 40 minutes; beyond these lead times, they lose their ability to forecast precisely. This finding is in line with the general features of the convective events, which can be characterized by large spatial and temporal variability, in magnitudes of tens of minutes and tens of kilometers.
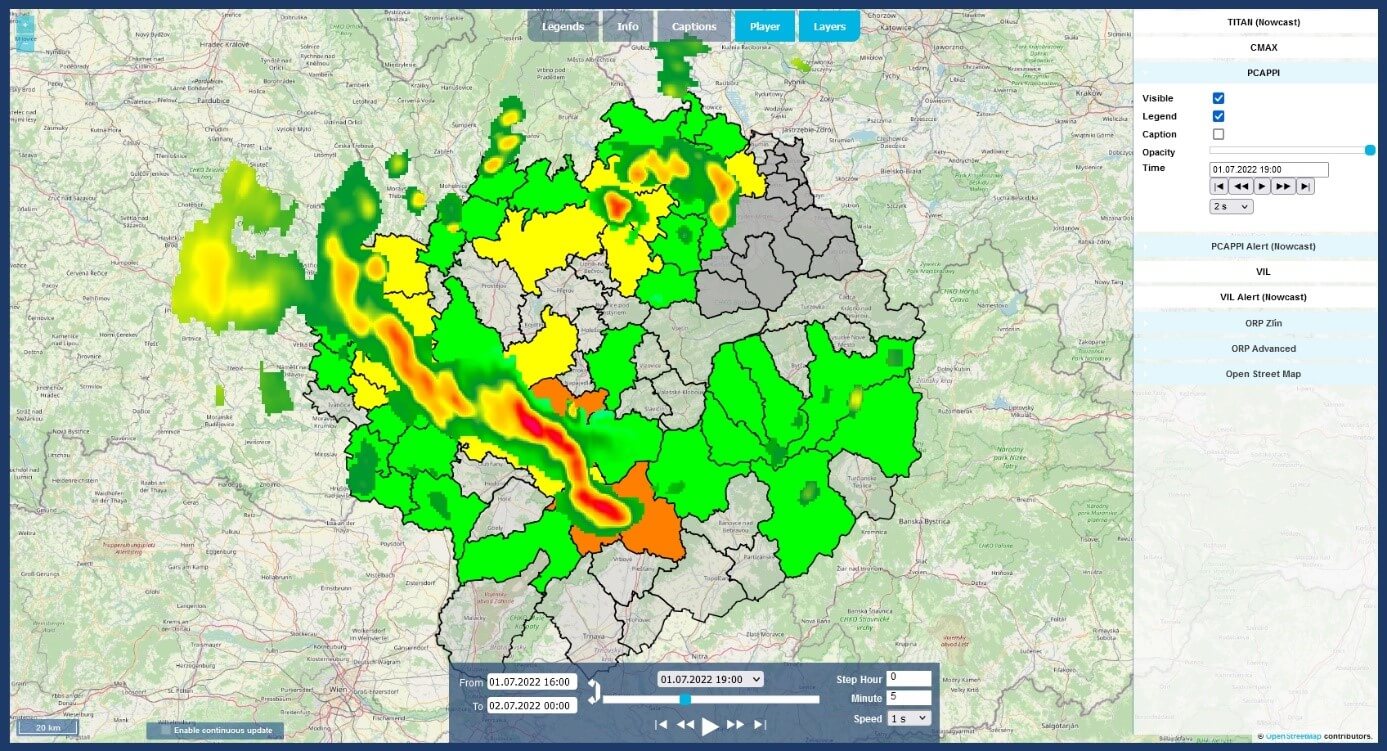
The main outcome of the project is a web application with a convenient user interface. The user can choose to display different meteorological information by turning on/off the different layers on the right side of the application:
- TITAN (Nowcast) – rainfall nowcasting based on the TITAN approach;
- CMAX – standard radar reflectivity product ColumnMax;
- PCAPPI – standard radar reflectivity product Pseudo Constant Altitude Plain Position Indicator;
- PCAPPI Alert (Nowcast) – the current state and rainfall nowcasting based on the developed machine learning approach, utilizing the radar reflectivity product PCAPPI;
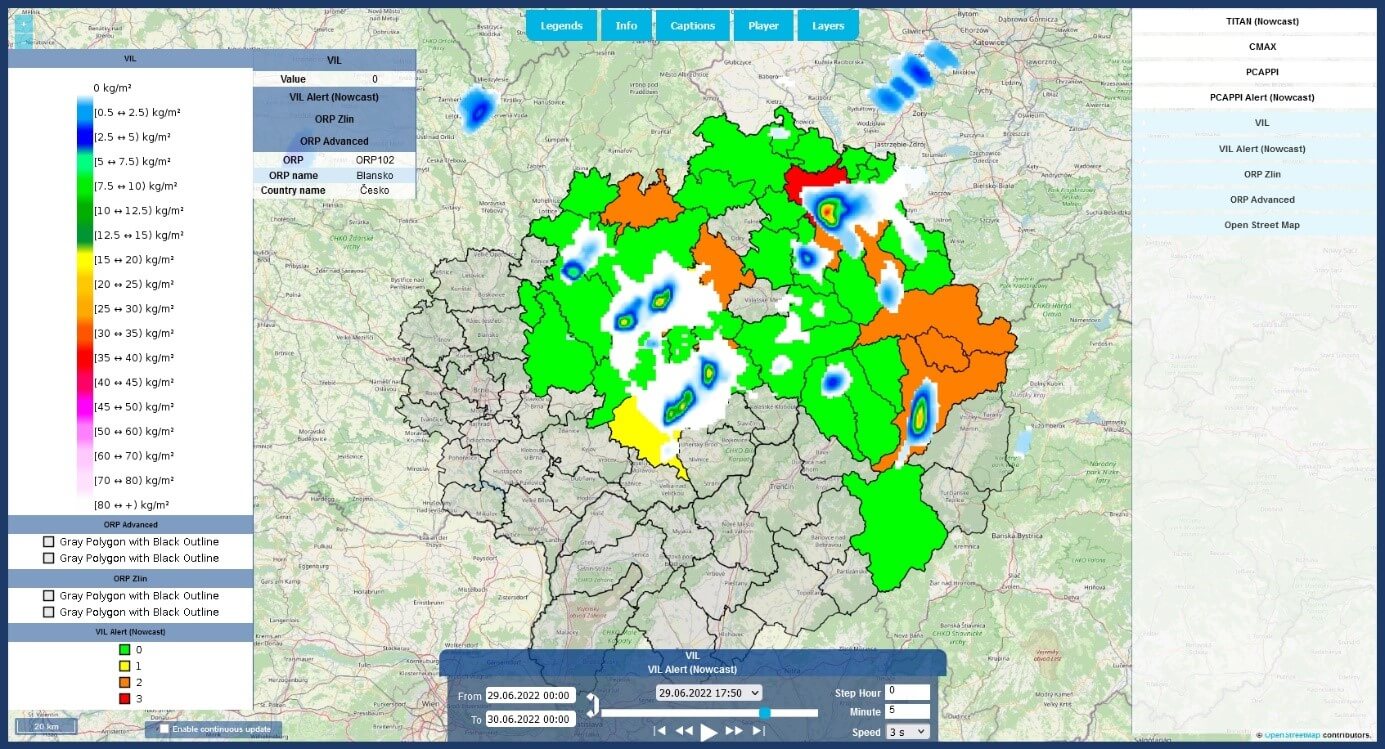
- VIL – standard radar reflectivity product Vertically Integrated Liquid;
- VIL Alert (Nowcast) – the current state and rainfall nowcasting based on the developed machine learning approach, utilizing the radar reflectivity product VIL;
- ORP Zlín – the boundaries of the 13 MEPs of the target region;
- ORP Advanced – the boundaries of the MEPs (in Czechia) and districts (in Slovakia) adjacent to the target region;
- Open Street Map – the basic background map.
The application allows work in continuous mode. If the user selects the preferred layers and checks the "Enable continuous update" box, the system will automatically display the latest meteorological fields as soon as the latest radar volume scan and processed radar products are available, usually at 5-minute intervals. The continuous mode option applies to both the current radar status and the nowcasts. The application also has a built-in player that can play a sequence of selected recent radar images according to the user's preferences.
The illustrated manual written in the Czech language, adapted to users from the target region, offers a detailed description of all the functions of the application.