
LINET systems enables customers to procure and operate their own, independent, ultra-precise and reliable lightning detection system. LINET does not only measure the position of the lightning stroke. LINET measures the electromagnetic radiation emitted by lightning strokes by highly sensitive lightning sensors. LINET captures the strength and polarity of the lightning strokes, and the height of intra-cloud strokes, in particular, expanding the lightning information to include a third dimension.
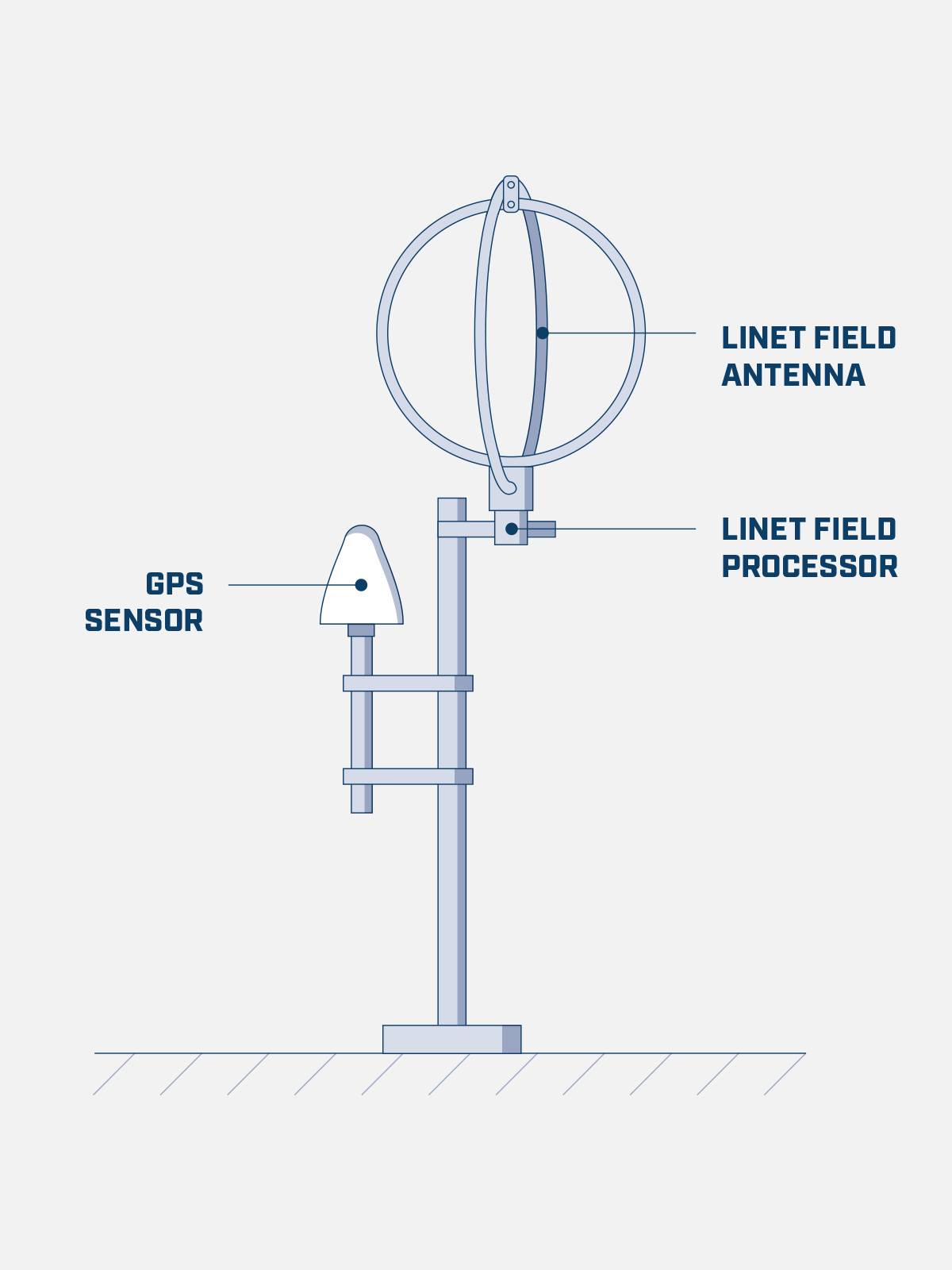
LINET essentially comprises two modules: several lightning sensors and a central server. The lightning sensors consist of one magnetic field antenna, a GPS module and a field processors and are set up at distance of app. 150 to 250 km. The position of the LINET Field Processor is of little importance as long as a sufficiently fast and stable internet connection is available. The redundant number of sensors constitutes a great advantage given that only the best signals will be included in the calculation. If an individual sensor does not work it is of no consequence to the overall quality of the lightning detection system.
Within a regular LINET lightning detection network lightning strokes are located with a statistical accuracy of better than 75 meters (mean value, low scattering). The quality is ensured by comparing the LINET data with selected cloud-to-ground strokes to towers of a known geographical position.
Thunderstorms normally occur in sharply delineated areas. This allows them to be easily grouped into storm cells, which are then depicted as a geographical polygon. LINET algorithm calculates storm cells in real-time. With every new lightning stroke, the cell is updated with respect to all its parameters. If a new storm cell is tracked for a few minutes, further parameters arise such as the speed of the path taken by the storm as well as direction and development of the thunderstorm. This information forms the basis for nowcasting. The length of the nowcasting depends on the intensity and tendency of the thunderstorm.